Facial Trauma
Any physical injury to the face is referred to as facial or maxillofacial trauma. Facial trauma can include soft tissue wounds like burns, lacerations, and bruises, fractures of the nasal bones, jaw fractures, and trauma to the eyes. Symptoms are particular to the type of damage; for example, fractures may involve pain, swelling, loss of function, or changes in the contour of facial tissues. A facial injury could result in loss of function and disfigurement, such as blindness or difficulties moving the jaw. A major issue in therapy is making sure that the airway is open and not threatened so that the patient can breathe, despite the fact that facial injuries are rarely life-threatening. This makes it important that the problem is addressed at the soonest by a specialist.
Common Causes of Facial Injuries
The following are common reasons for facial injuries:
- Auto and motorbike collisions
- Sports injuries and wounds
- Violence
Types of Facial Fractures
Nasal Bone Fractures (Broken Nose)
The most frequent kind of facial fracture is a nasal bone fracture. Bruising around the nose and nosebleeds are typical signs of a nasal fracture. If the displacement of the fractured nasal bones is enough to cause a deformity or interfere with breathing, the repair is advantageous. Most nasal fractures require a closed nasal reduction for repair.
An injured nose may exhibit the following signs:
- Purple skin patch brought on by blood leaking from blood vessels
- “Black eyes” refers to discoloration under the eyes
- Obstruction in either or both nostrils or a misaligned septum
- A bridge with an indent or a twisted nose
- Nosebleed
Fractures of the Frontal Bone
The frontal bone and sinus floor may fracture due to a head injury with high impact. The center of the forehead is the most fracture-prone area. The bone is the weakest and thinnest in that area. An injury could leave the bone with an indentation.
Fractures of the Zygomatic Maxillary Region (Cheeks/Upper Jaw)
The upper jaw (maxilla) and skull bones are connected to the zygomas (cheekbones) at various places. Cheekbone fractures may cause neighboring facial bones to shatter.
Orbital Fractures
An orbital fracture may cause the following symptoms:
- Blurry, diminished, or distorted vision
- Difficulty shifting the gaze up, down, left, or right
- Swelling under the eyes, on the cheeks, or the forehead
- Protruding or drooping eyes
- Facial numbness close to the wound
- The white of the eye has blood or other stains
Injury to the orbit (eye socket) must be treated quickly or the muscles involved could become permanently scarred.
Lower Jaw Fractures
The mandible, which moves while you talk or chew, maintains the lower teeth in place. Lower jaw fractures can happen anywhere along the bone, including the body, the angle, the condyle, and the connection between the two sides of the lower jaw. Arch bars are typically required to connect the jaws together. The broken bone pieces are then secured using plates.
Signs and symptoms of upper or lower jaw fracture:
- Difficulty speaking, chewing or eating
- Loose, damaged, or missing teeth
- Teeth that don’t fit together properly
- When you open your mouth, your cheek hurts
Treatment and Diagnosis
Patients with facial fractures are evaluated and treated in the emergency room. Typically, imaging in the form of a computed tomography (CT) scan is necessary for the final diagnosis. This helps with fracture diagnosis and therapy planning. Most patients with facial fractures can be treated as outpatients at the surgeon’s office. Surgery is normally performed one to two weeks following the injury if required. This window of time allows the face swelling caused by the initial damage to subside significantly, making the surgery safer and more accurate. The risk of malunion is increased by delaying too long (greater than two to three weeks).
Radiant Maxillofacial Surgical Centre and Dental Clinic
Radiant Maxillofacial Surgical Centre and Dental Clinic has an emergency facility to treat various facial fractures. Dr Bharat Choudhary is a trained and skilled oral surgeon. He is a consultant at various hospitals and clinics. He has been handling facial trauma cases with utmost care and is one of the few dentists to provide treatment for the same in Bhayandar.
Facial Trauma - Dr Bharat Choudhary Radiant Dental Clinic, Mira road, Mumbai
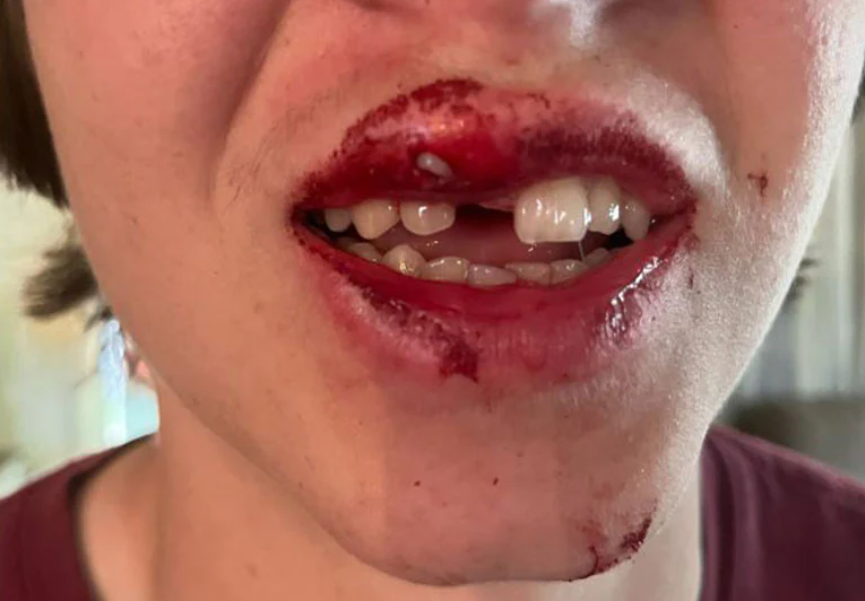
Facial trauma treatment by skilled oral surgeon Dr. Bharat Choudhary at Radiant Dental Clinic, Mira Road, Mumbai. Expert diagnosis and treatment for various facial fractures.
Service Type: DENTAL SERVICES
